IDENTIFYING DISADVANTAGED COMMUNITIES AND THE WATER SYSTEMS THAT SERVE THEM

Identifying Disadvantaged Communities
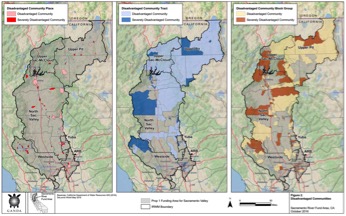
The first step as part of the Sacramento River Funding Area (SRFA) Disadvantaged Community Involvement Program (DACIP) was to identify the disadvantaged communities (DACs) to target for outreach. The SRFA DACIP Project Team used the Department of Water Resources’ DAC Mapping Tool to identify DAC Places, Census Tracts, and Block Groups, using 2014 American Community Survey data. A total of 91 DAC Places were identified within the SRFA. Next, the SRFA DACIP Project Team identified and created a database of water purveyors servicing the communities in each DAC Census Place. Click on this link to download the list of DAC Places
What is A DAC?
A “Disadvantaged Community” (DAC) is a community with an annual median household income (MHI) that is less than 80% of the statewide annual MHI. In 2017 the statewide annual MHI was $67,169; therefore households earning less than $53,735 are considered DAC. For the purposes of the DAC Involvement Program (DACIP), DWR uses the term “DAC” to refer collectively to: economically distressed areas (EDAs), underrepresented communities, and disadvantaged communities. DWR has developed a DAC Mapping Tool that allows users to visually locate DACs in California..
What is An EDA?
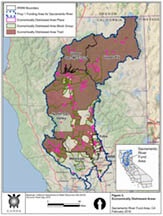
DWR defines “Economically Distressed Area” (EDA) as a municipality with a population of 20,000 persons or less, a rural county, or a reasonably isolated and divisible segment of a larger municipality where the segment of the population is 20,000 persons or less, with an annual median household income (MHI) that is less than 85% of the statewide MHI, and with one or more of the following conditions: (1) financial hardship, (2) Unemployment rate at least 2% higher than the statewide average, or (3) low population density. DWR has developed an EDA Mapping Tool that allows users to visually locate EDAs in California.
DAC Places, Census Tracts, and Block Groups in the SRFA and
Economically Distressed Areas in the SRFA
click to enlarge maps
Identifying Small Water Systems Servicing DACs
Many DAC Communities within the SRFA are served by large, public water systems that have adequate staff and capacity to provide drinking water and wastewater services and to comply with all state regulations. However, in the highly rural SRFA, possibly more DAC people are served by small water systems, run by volunteer boards with no full-time staff that struggle to maintain their infrastructure, cope with emergencies and stay in compliance with all of the rules and regulations. In order to better understand this population of DAC small water systems, the SRFA DACIP Project Team first had to identify them. The Project Team created a database of all small water systems located within DAC Places, Census Tracts and Block Groups. Several data sources were used to identify these small water systems in the SRFA. The project team obtained water system and service boundary information primarily from the State Water Resources Control Board and from “Local Primacy Agency” (LPA) counties (i.e., counties to which the SWRCB has delegated its regulatory authority over public drinking water systems; eleven counties in the SRFA have LPA authority, six do not).
What is a “Small Water System”?
“Small water system” is defined as a system that provides water for human consumption through pipes or other constructed conveyances to at least 5 service connections, but no more than 3,299 service connections, or serves an average of at least 25 people for at least 60 days a year. This includes:
- “State small water systems” that serve between 5 – 14 service connections used by yearlong residents, and that regularly serve not more than 25 yearlong residents;
- “Community water systems” that serve at least 15 service connections used by yearlong residents or that regularly serve at least 25 yearlong residents;
- “Non-transient non-community water systems” such as a school, labor camp, institution, or place of employment, that regularly serve at least 25 of the same persons over six months per year;
- “Transient non-community water systems” such as hotels and restaurants, that do not regularly serve at least 25 of the same persons over six months per year.
The Project Team consulted with LPA counties to obtain data for small water systems with less than 200 connections, and with the State Water Board for systems with less than 200 connections in non-LPA counties and for all small water systems with more than 200 connections. County environmental health department representatives were also interviewed for additional information regarding the small water systems.
The SRFA DACIP Project Team identified approximately 662 small water systems within the six IRWM regions of the SRFA; approximately 429 of those systems specifically serve DAC areas, with an estimated DAC population of approximately 195,500 residents. These community water systems serve residential areas, mobile home parks, RV parks, schools, parks, and churches. Transient small water systems were also included in the database, and serve employees and customers including gas stations, food markets, and businesses.
The SRFA DACIP Project Team created a complete DAC Small Water System Database, organized by IRWM region, as well as maps, which were distributed to each IRWM for outreach. The table below provides an overview of the types of small water systems located in each IRWM region of the SRFA
Overview of Small Water Systems in the SRFA
IRWM
|
Small
|
DAC
|
||||
|
<200
|
Community
|
Non-transient
|
Transient
|
Total
|
||
|
Upper |
5 |
0 |
1 |
12 |
18 |
1,396* |
|
Upper |
12 |
3 |
3 |
33 |
51 |
16,149* |
|
North |
117 |
4 |
58 |
66 |
245 |
123,177* |
|
Westside |
31 |
10 |
2 |
28 |
71 |
51,205 |
|
Yuba |
10 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
12 |
716 |
|
American |
9 |
0 |
4 |
19 |
32 |
2,842 |
|
TOTAL SRFA |
184 |
17 |
70 |
158 |
429 |
195,485* |
The SRFA DACIP Project Team produced a Phase I Summary Report on Small Water Systems that describes this process and the outcomes in detail. Click here to download the SRFA DACI Phase I Final Report